|
|  |
| WASHINGTON — President Obama on Wednesday ordered the restoration of full diplomatic relations with Cuba and the opening of an embassy in Havana for the first time in more than a half-century as he vowed to “cut loose the shackles of the past” and sweep aside one of the last vestiges of the Cold War. The surprise announcement came at the end of 18 months of secret talks that produced a prisoner swap negotiated with the help of Pope Francis and concluded by a telephone call between Mr. Obama and President Raúl Castro. The historic deal broke an enduring stalemate between two countries divided by just 90 miles of water but oceans of mistrust and hostility dating from the days of Theodore Roosevelt’s charge up San Juan Hill and the nuclear brinkmanship of the Cuban missile crisis. “We will end an outdated approach that for decades has failed to advance our interests, and instead we will begin to normalize relations between our two countries,” Mr. Obama said in a nationally televised statement from the White House. The deal, he added, will “begin a new chapter among the nations of the Americas” and move beyond a “rigid policy that is rooted in events that took place before most of us were born.” Continue reading the main storyVideo
The president outlined the steps the United States would take to “end an outdated approach” and begin to normalize relations with Cuba. In doing so, Mr. Obama ventured into diplomatic territory where the last 10 presidents refused to go, and Republicans, along with a senior Democrat, quickly characterized the rapprochement with the Castro family as appeasement of the hemisphere’s leading dictatorship. Republican lawmakers who will take control of the Senate as well as the House next month made clear they would resist lifting the 54-year-old trade embargo. “This entire policy shift announced today is based on an illusion, on a lie, the lie and the illusion that more commerce and access to money and goods will translate to political freedom for the Cuban people,” said Senator Marco Rubio, a Republican from Florida and son of Cuban immigrants. “All this is going to do is give the Castro regime, which controls every aspect of Cuban life, the opportunity to manipulate these changes to perpetuate itself in power.” For good or ill, the move represented a dramatic turning point in relations with an island that for generations has captivated and vexed its giant northern neighbor. From the 18th century, when successive presidents coveted it, Cuba loomed large in the American imagination long before Fidel Castro stormed from the mountains and seized power in 1959.
Mr. Castro’s alliance with the Soviet Union made Cuba a geopolitical flash point in a global struggle of ideology and power. President Dwight D. Eisenhower imposed the first trade embargo in 1960 and broke off diplomatic relations in January 1961, just weeks before leaving office and seven months before Mr. Obama was born. Under President John F. Kennedy, the failed Bay of Pigs operation aimed at toppling Mr. Castro in April 1961 and the 13-day showdown over Soviet missiles installed in Cuba the following year cemented its status as a ground zero in the Cold War. Photo
Students celebrated in Havana after news that Washington had released three Cuban spies in a prisoner exchange. CreditRoberto Morejon/Agence France-Presse — Getty Images Continue reading the main story But the relationship remained frozen in time long after the fall of the Berlin Wall and the collapse of the Soviet Union, a thorn in the side of multiple presidents who waited for Mr. Castro’s demise and experienced false hope when he passed power to his brother, Raúl. Even as the United States built relations with Communist nations like China and Vietnam, Cuba remained one of just a few nations, along with Iran and North Korea, that had no formal ties with Washington. Mr. Obama has long expressed hope of transforming relations with Cuba and relaxed some travel restrictions in 2011. But further moves remained untenable as long as Cuba held Alan P. Gross, an American government contractor arrested in 2009 and sentenced to 15 years in a Cuban prison for trying to deliver satellite telephone equipment capable of cloaking connections to the Internet. After winning re-election, Mr. Obama resolved to make Cuba a priority for his second term and authorized secret negotiations led by two aides, Benjamin J. Rhodes and Ricardo Zúñiga, who conducted nine meetings with Cuban counterparts starting in June 2013, most of them in Canada, which has ties with Havana. Pope Francis encouraged the talks with letters to Mr. Obama and Mr. Castro and had the Vatican host a meeting in October to finalize the terms of the deal. Mr. Obama spoke with Mr. Castro by telephone on Tuesday to seal the agreement in a call that lasted more than 45 minutes, the first direct substantive contact between the leaders of the two countries in more than 50 years.
Cuba Moves Toward CapitalismHAVANA – When Cuba legalizes buying and selling real estate by the end of the year – as the government promised again this week – many expect a cascade of changes: higher prices, mass relocation, property taxes and a flood of money from Cubans in the United States and around the world. Private property is the nucleus of capitalism, of course, so the plan to legitimize it here in a country of slogans like “socialism or death” strikes many Cubans as jaw-dropping. Indeed, most people expect onerous regulations and, already, the plan outlined by the state media would suppress the market by limiting Cubans to one home or apartment and requiring full-time residency. Yet even with some state control, experts say, property sales could transform Cuba more than any of the economic reforms announced by President Raul Castro’s government. Cuba under Raúl: Creeping toward capitalism?Since Raúl Castro took the helm in February, he's rolled out a series economic changes, including allowing Cubans to buy cell phones and giving farmers profit-incentives.
Clandestine gym: Guillermo Arrastia built exercise equipment out of old scaffolding. He runs this illegal gym in a Havana garage. Havana A handful of Cubans are taking turns doing bicep curls and pedaling on stationary bikes. At first glance, there's nothing extraordinary about this nameless gym in the basement of a Havana apartment complex.
Yet when night falls, the machines – crafted out of wood planks and scavenged metal tubing – disappear like a government informant into the shadows. They are disassembled and tucked away to make room for the coughing Russian Ladas and '50s-era American cars that fill the building's parking lot. Officially, this fly-by-day gym does not exist, but Guillermo Arrastia opened it five years ago. He employs a staff of three and collects monthly $5 fees from more than 100 members. It is run completely "por la izquierda" – "on the left" – a term that describes how most Cubans make ends meet. "We have to survive," says Mr. Arrastia, unapologetically.
The island nation's economy has struggled mightily since losing the support of the Soviet Union in the early 1990s. Free-market reforms within a socialist system, like the kind embraced by China, had been rejected by Fidel Castro, who ruled for a half century. But there are signs that younger brother Raúl, who permanently replaced Fidel in February, may orchestrate a move toward a more capitalist economy. Raúl's reputation as a pragmatist is unfurling expectations here that the era of asceticism and austerity is coming to a close. Major agricultural reforms have been unveiled. And in a speech earlier this month, he seemed to be preparing the populace for an economic shift. "Socialism means social justice and equality, but equality of rights, of opportunities, not of income," Raúl said on July 11 while addressing Cuba's rubber-stamp parliament in its first session since he replaced Fidel. "Equality is not egalitarianism." It's hard to imagine the father of the 1959 revolution ever uttering such words, say Cuba analysts. And a recent flurry of headline-grabbing changes – such as allowing Cubans to patronize tourist hotels and to own cellphones, DVD players, and computers – is fueling speculation about how fast Raúl will pursue the "China model" of a managed creep toward free markets. Some expect more reforms to be announced during a speech by Raúl on July 26, Revolution Day. "Cuba is never going to go as far as the Chinese have in dismantling the social safety net," says William LeoGrande, a Cuba expert at American University in Washington. But he says that Raúl has already exhibited an expediency that Fidel never dared: acknowledging under-the-table wages, raising salaries and enticing productivity with payment, and, most important, he says, introducing market incentives in the farming sector that could be the starting gun for reforms in other sectors. "To some extent, they are experimenting to see how additional market mechanisms work out economically and to see the political ramifications," he says. "I think there are a lot more changes coming." After the Soviet Union collapsed – and Cuba lost generous oil supplies and subsidies that had buoyed the economy for decades – a "special period" of economic hardship ensued. In this context, Fidel grudgingly loosened the economy, giving rise to a new crop of tailors, mechanics, and restaurateurs. The government created about 150 categories of licenses for Cubans to start their own businesses, and the ranks of self-employed swelled to 200,000. Today that number has fallen to 150,000, says Antonio Jorge, a retired economics professor from Florida International University who also worked as a finance official in the early years of Fidel's reign. Fidel began to discourage such businesses the late 1990s, saying that they were creating economic inequality, says Mr. Jorge. A gap was growing between entrepreneurial haves and state-employed have-nots. In response, the government stopped issuing new licenses for 40 categories of businesses (including restaurants) in 2004, jacked up taxes, and created other limits on income growth, such as reducing the number of tables permitted atpaladares – private restaurants that Cubans are allowed to run out of their homes. Jorge says that Fidel wouldn't allow anything that detracted from absolute central government control. But, he says, that Raúl could, for example, boost the number of categories of small businesses and be more liberal in the granting of licenses, or remove some of the barriers such as high taxes. "These are measures that won't affect his hold on power or change the collectivist nature of the regime, but will improve standards of living for some people," says Jorge. But for now, the burdens Fidel imposed have merely pushed entrepreneurial activity underground. Ani, a 20-something Cuban woman – who like most Cubans interviewed for this series withheld her last name – has opted out of the state jobs system, one that she once idealistically embraced, she says. She was trained as a teacher in her home province Pinar del Rio, and moved to Havana to teach junior high students. But after a few years of making 200 pesos ($9) a month, she quit. "The [pay for the] job was not worth it," she says. Now she has no official job, aside from helping her aunt rent out a room to foreign tourists, an illegal but far more lucrative venture. When asked about the loss of her contribution to society as an educator, she shrugs: "This is how it works here. What we don't have we invent." Everything is 'on the left'It takes no more than a half day with Jorge Aviles to see that nearly everyone in his Havana neighborhood, and in his sphere of activities, operates "on the left." There is the neighbor who rents out her empty apartment to foreign tourists – even though by law to rent a room in your house you must live there. There is another who sells pizzas out her side window at night. As Mr. Aviles walks down the street, he gets "business" proposals, ranging from risky to innocuous. One a recent day, he bumps into an old friend and is offered a year's supply of soap bars for $75. He counters by offering the spare room he sometimes rents by the hour to couples. The friend replies that he and his girlfriend have recently gotten their own place. How about an installment plan of $25 a year for three years, he asks. Aviles passes. "Everything here is about selling and negotiating, and it's all illegal," says Aviles, who insists on using a pseudonym since he is on the government's radar after being fined in November for renting his room to foreign tourists without authorization. He questions why endeavors that would be considered entrepreneurial and encouraged in most countries are outside the law here. Back at his underground gym, Arrastia also knows he faces a fine if he is found out. After he lost his computer sales job and hit on the idea of a gym in the parking lot, he sought a government license for his gym. But he found out that the business category doesn't exist. So he consulted his building's neighborhood association, which approved of his plans. Today he pays the association about $12 a month to keep quiet about the arrangement. He knows he is at the mercy of any disgruntled neighbor, but he also says that such endeavors will be legalized and that his tiny exercise room with about 25 homemade machines will be the template for a much bigger business some day. "I do believe this will be authorized," says Arrastia. "I want to have another much bigger gym, legally.... I will grow this business and have gyms all over Havana." Farm reform on fast trackHow soon, if ever, urban Cubans like Arrastia will get the opportunity to legally run small businesses isn't clear. But Cubans in the countryside may already be on a faster track to change. Agricultural reforms could radically transform the island's economy: Last week, Raúl granted private farmers the right to till plots of up to 99 acres of unused government land. This follows a previous announcement to shift control of farms from the central government in Havana to local councils, raise prices for certain products to boost production, and give farmers the right to use whatever farm equipment they can afford to buy. Almost immediately upon taking power 50 years ago, Fidel Castro began nationalizing the telecommunications industry and expropriating farm lands. Less than a decade later almost all businesses were in state hands. In exchange, Cubans were given subsidized food, free healthcare, and homes. The economy never functioned independently, and it has never quite recovered from the fall of the Soviet Union. Cuba now relies heavily on Venezuela, whose leftistPresident Hugo Chávez sends nearly 100,000 barrels of oil a day to the island in exchange for social services, such as Cuban doctors and teachers. Even though Raúl promises not to veer from the ideals of the revolution, he has publicly acknowledged that the system does not work in its current form. The moves to increase crop production are, in part, a response to a global spike in fuel and food prices, which has made the subsidized food system – once regarded as one of the major successes of the revolution – untenable for many ordinary Cubans today. "We're [in deep trouble]," whispers a man, using an expletive, while exiting a state-run produce market in Havana. He says he could not afford to buy anything to supplement the monthly ration of rice, beans, potatoes, eggs, a little meat, and other goods. Many Cubans say the ration does not last them more than three weeks, if that. In his most recent speech to parliament, Raúl implored his countrymen to work harder and prepare for tough times ahead as the global food crisis ripples toward Cuba. "We have to definitively reverse the decline in the amount of cultivated land," he said, adding that it has shrunk by 33 percent in the past nine years. "Stated simply, we must return to the land. We must make it produce. There is already a clear strategy and a plan of action, from the national level to the lowest level of production." Currently more than half of arable land lies fallow or is under used, according to Cuban government figures cited by The Associated Press. Cuba spent $1.5 billion importing food last year. This year it is expected to spend $1 billion more, say officials. "There's been a recognition by Raúl that the government cannot run farms as well as [private] firms can," says John Parke Wright, a wealthy rancher and sixth-generation Floridian whose ancestors were instrumental in cementing trade ties between Tampa and Havana in the 1800s (see sidebar, page 11). Mr. Wright and other longtime observers say that market experiments on farms are just a stepping stone to a more open economy. Texan cattle and cottonBut while some Cubans blame their economic woes on strict controls and prohibitive taxes, many still view the USand its 1962 trade embargo as the bigger culprit. No matter how much Raúl seeks to open the economy, the embargo will stand in the way of much-needed foreign investment, analysts say. If the economy is opened up, the tourist industry will explode. But it is on the farms and fields of Cuba where a change is most likely – and there is no shortage of investors eyeing potential changes. On May 27, a group of trade representatives from Texas wrapped up the first official state visit to the island since the US established the embargo. "Cubans expressed a sincere desire to do business with Texas," says Texas agriculture commissioner Todd Staples, who led the delegation. Cuba is an important market for Texan cattle, rice, poultry, cotton, and processed food products that enter under provisions in the US embargo that allow small amounts of trade in agricultural products. "We just went to develop relationships, but the trip exceeded our expectations," says Mr. Staples. Members of the delegation signed two new cotton contracts worth $400,000 and initiated several other contracts for poultry, milk, and processed foods. "Positive trade relationships can lead to greater understanding of the issues that divide us," he says. Such goodwill may not be the status quo in either nation right now, but the sense that change is coming certainly is. "The social values we espouse mean nothing if there is no economic basis," says Renel, a young lawyer in Havana. "Whether it is socialism, communism, capitalism, even feudalism, things are going to change." Squatting to fix one of his broken-down stationary exercise bikes, Arrastia agrees: "In the future, the economy will open up. It has to. The people have a limit." Marxism demands the abolition of private property as one of the most important points in the move away from the free market so allowing it is surely a sign that Cuba is now moving closer to capitalism. In all fairness Cuba does allow people to ‘sell’ for example their house but it more closely resembles a complicated system of bartering and government monitoring through officials that usually need to be bribed. It’s more like a state sponsored trade where the government acts like the mafia and demands a cut of the profit. What does this mean for the Cuban people? For the first time since the revolution Cubans can now they say they own their house or a piece of land. This could trigger the most rudimentary market, cause Cubans to recognise this as their right and cut out the state from the process of allowing individuals to buy, sell and exchange their property for goods or services. I’ve just inadvertently made an assertion that is pivotal in the next section: that Cubans have the right to own property and the state should be cut out of the process of buying or selling it. There are several human rights that would support the presence of a free market in property, the right of individuals to own things and the right to be left alone by the state when you’re conducting private business.
Article 17 of the Declaration explicitly states we have the right to own property; therefore there is no reason why we cannot buy and sell things, the basis of the free market. I am unimpressed by the Cuban Government’s statement that it will ‘allow its people to own property’. It simply isn’t empowered to say which human rights Cubans do or don’t have. Cuban people have always had the right to own property and the right to be left alone by the state; the Cuban Government just didn’t respect it. I don’t think we should dismiss this important move towards greater freedom for Cubans simply because ‘they’ve always had it’ but I don’t think we should stand up and applaud Raul Castro for not denying his people their human rights. We wouldn’t say ‘well done’ if he announced that the Cuban Government had decided not to deny the people the right to life would we? It’s an extreme parallel to draw but human rights are indivisible, you can’t have one without the others. The right to life is part of the right to property and vice versa. They are also interdependent, they rely upon each other.
The right to property is one that comes up against attack from left of centre governments and ideologues more often than the others. They claim ‘property is theft’, ownership is taking away from the environment or property instead of being an individual right is a collective right belonging to society. All of these arguments have their merits but simply put, guaranteeing the right to property, with all its inherent connotations such as buying or selling goods or services, is guaranteeing equality in a market economy. Let me give some examples, the right to property prohibits a person of one ethnicity refusing to sell their home to a person of another. The buyer is human being therefore has the right to own property. It prohibits a gay person being refused service in a restaurant, that person is a human being therefore has the right to buy a service. It prohibits women being denied inheritance, she is a human being therefore has the right to own land and to receive and pass it on without interference.
A wheelchair user can expect an access ramp into a cinema because they have an equal right to use the service as someone who can take the stairs. To paraphrase: the right to own property is not just the right to acquire a house, it’s the right of all human beings to participate in a market as equals, irrespective of any personal defining characteristic. The right to own property might be arguably the most capitalist of our human rights, it’s inextricably tied to the market and ownership, but it is also a great equalizer and without knowing it I am sure many of us invoke it every day.
The seafront at Havana. Cubans are having to deal with the possibility of widespread redundancies as the state struggles to manage a mixed economy. Photograph: Desmond Boylan/Reuters It was supposed to be the start of a brave new world in which the customer was king. But the teenage boy in the barber's chair stared at his reflection, aghast and almost crying. "What have you done?" he asked, caressing uneven clumps on a shorn scalp. The barber, a fortysomething man with a grubby white coat, put down the scissors, lit a cigarette, and shrugged. "Looks OK to me. Don't know what you're on about." The young customer examined his head from different angles, each worse than the last. "It's like …" – he struggled for words – "a tennis ball. A bald bloody tennis ball." The barber took another drag and put out his hand. "Forty pesos. Have a nice day." The scene on Neptuno street, a crumbling, sun-bleached quarter near downtown Havana, was a taste of Cuba's challenge in transforming its socialist economy with a sweeping privatisation drive. Authorities announced yesterday they will lay off more than 1 million state employees in the island's biggest economic shake-up since the 1960s. Cuts begin immediately, with 500,000 jobs due to go by March. Loosened controls on private enterprise will, it is hoped, jumpstart the private sector and turn former public workers into entrepreneurs. "Our state cannot and should not continue maintaining companies, productive entities, services and budgeted sectors with bloated payrolls [and] losses that hurt the economy," said the official Cuban labour federation, which announced the news. "Job options will be increased and broadened with new forms of non-state employment, among them leasing land, co-operatives and self-employment, absorbing hundreds of thousands of workers in the coming years," it said. In fact, the changes started in April with a pilot scheme to privatise barbers and hairdressers. Formerly state employees – about 85% of the labour force works for the communist state – they were told to take over their own salons, charge whatever they wanted, pay tax – and court customers. As the barber showed, providing good customer service, let alone expanding market share, is an alien concept to many accustomed to receiving the same pittance wage regardless of job performance. "I don't want to take over this place," Luis, the barber, who preferred not to give his surname, told the Guardian. "How do I know it'll make a profit? How do I pay suppliers?" Like it or not, those are questions many more Cubans will soon be asking after receiving their pink slips. The authorities, according to a 26-page party document leaked to the Associated Press, have a plan for them to raise rabbits, paint buildings, make bricks, collect garbage and pilot ferries across Havana's bay. Some of those let go will be urged to form private co-operatives, others will be directed towards foreign-run companies and joint ventures, and others will be encouraged to set up their own small businesses. The Communist party document admitted lack of experience, insufficient skill levels and low initiative could sink new enterprises. "Many of them could fail within a year," it says. After half a century of official certitude about being its socialist course, Cuba is entering new waters. Its final destination remains unclear. "A hybrid is evolving which can't be said to be any one thing," said Julia Sweig, a Cuba expert at the Council on Foreign Relations thinktank. "We're seeing a uniquely Cuban transition but within the global economy." Unemployment last year was officially 1.7%, but with average monthly salaries of only $20, supplemented by a ration book and free health care and education, many Cubans make minimal efforts, prompting an old joke: "They pretend to pay us and we pretend to work." Che Guevara's dream of creating a "socialist man" motivated by moral rather than material incentives has long been abandoned. This week's announcement – widely reported across state media – has been trailed since Raul Castro succeeded his brother Fidel as president in 2008. "We have to erase forever the notion that Cuba is the only country in the world in which people can live without working," he told the national assembly last month. The decades-old US embargo – a crippling, punitive measure – could no longer be blamed for all the island's woes, he said. It was no longer possible to protect and subsidise salaries on an unlimited basis and cuts will affect all government sectors, said the labour federation. "Losses that hurt our economy are ultimately counterproductive, creating bad habits and distorting worker conduct." Workers at the ministries of sugar, public health, tourism and agriculture will be let go first, according to the Communist party document. The last in line will be those at civil aviation and the ministries of foreign relations and social services. To ease the pain, authorities hope to energise the stunted private sector by encouraging Cubans to raise animals, grow vegetables, drive taxis, repair vehicles, make sweets and dried fruit and seek building work. Leftwingers abroad may feel let down by the cuts, but Cuban officials believe the thriving black market is an indicator that the private sector will soak up surplus labour. Such consensus would contrast with Britain, Ireland and Greece, among others, where cutbacks have triggered vocal protests. One Havana-based western diplomat was less sanguine about Cuba's response, especially as there were simultaneous cuts in subsidies for food, cigarettes and other products which people used to barter. "People knew this was coming, but now it's here, it's real, and they're worried. Bosses will get rid of the least productive employees, the ones who don't work or show up for work. The type of people who may lack the get up and go to start a business. People wonder if there will be a rise in crime, or social protests." Europe was enduring its own economic travails but was at least accustomed to unemployment, said the diplomat. "People here aren't used to being threatened with losing their job. They may complain their salary is only $15 a month, but that's $15 more than nothing." The US journalist who elicited Fidel Castro's apparent admission that Cuba's economic model does not work has insisted the quote accurately reflected the former president's views. Castro confirmed uttering the nine-word remark,, which caused widespread astonishment, but said he had been misinterpreted and that he had meant the "exact opposite". At the end of a lunch in Havana Castro told Daniel Goldberg, a correspondent with the Atlantic magazine: "The Cuban model doesn't even work for us anymore." The comandante was in full flow, touching on many different topics at the same time, said Goldberg. "I don't want to call it a throwaway line but it was kind of semi-stream of consciousness." Goldberg said he was surprised at Castro's subsequent attempt to explain away the remark. "I don't know how you can interpret that as its opposite. The 84-year-old had made similar admissions before, said the journalist, and economic changes underway on the island made it "a truism that the Cuban model isn't working". Julia Sweig, a Cuba expert who also attended the lunch, backed Goldberg's version and said Castro's apparent U-turn was aimed at a domestic audience. "He wanted to say that although we're changing our model that doesn't mean we're importing US-style capitalism," she said. Castro's spate of public appearances and comments, said Sweig, were "spontaneous" but fitted the economic reform strategy of his brother and successor, Raul Castro. It's never too late to learn. Current news from Spain, France, Iraq, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Iran, Syria, England, the Malvinas and several other parts of the planet are serious and all foretell political and economic disaster due to the foolhardiness of the United States and its allies.
|
|
Two decades ago, in the midst of rioting and anti-government protests in Cuba, Fidel Castro announced that 'whoever wanted to leave, could go'—indicating that his forces would not prevent refugees from fleeing the country. More than 35,000 took the opportunity to leave, most heading to the United States. Men, women, and children packed into small boats and makeshift rafts and set off for Florida in the largest exodus from Cuba since the 1980 Mariel Boatlift. Reuters photographer Enrique de la Osa recently caught up with some of those 1994 refugees in Miami, photographing them at work and at home in their new country, 20 years later. [20 photos] Use j/k keys or ←/→ to navigate Choose: 1024px 1280px Cubans leave their country in a makeshift wooden boat during a mass exodus of rafters in this August, 1994 photo. In mid-August 1994, after a string of boat hijackings, unprecedented rioting and the killing of a Cuban navy lieutenant prompted President Fidel Castro to suggest that those wanting to leave, could. Over about five weeks, more than 35,000 Cubans took Castro at his word and sailed away on makeshift rafts while authorities stood by. (AP Photo/Jose Goitia)
On September 7, 1994, people on a Havana street throng around a large raft as it is secured on the top of a truck before being transported to the beach to carry more refugees away from the country. (Doug Collier/AFP/Getty Images) #
Unidentified Cubans lower a raft into the water in this August 19,1994 photo, preparing to leave the Cuban coast in Cojimar, near Havana, during the 1994 mass exodus. (AP Photo/Jose Goitia,) #
People launch a makeshift boat into the Straits of Florida towards the U.S., on the last day of the 1994 Cuban raft exodus in Havana, in this September 13, 1994 photo. (Reuters/Rolando Pujol Rodriguez/Files) #
A Cuban man runs desperately to reach one of the last rafts to leave from Brissas Del Mar Beach, Cuba on September 11, 1994. The man was able to board the raft. (AP Photo/Jose Luis Magana) #
In this August 24, 1994 photo, Cuban refugees stranded on a makeshift raft float in the open sea about halfway between Key West, Florida, and Cuba, as the exodus from their homeland continued. (AP Photo/Hans Deryk) #
Members of the U.S. coast guard scramble to rescue a group of Cuban refugees after their raft capsized some 25 miles off the coast of Cuba on August 31, 1994. (Doug Collier/AFP/Getty Images) #
The Coast Guard Cutter "Monhegan" races away carrying 223 Cuban refugees rescued in the Florida Straits August 24, 1994. The 110-foot cutter was taking the refugees to another ship to be dropped off at the U.S. Navy Base in Guantanamo Bay. (Reuters) #
In 2014, former Cuban rafter Luis Soler, 53, poses with the two Emmy awards he won as creative director at the Univision TV network, in Miami, on September 23, 2014. Soler said he spent five days adrift with other migrants in 1994 before being picked up by the U.S. Coast Guard. (Reuters/Enrique de la Osa) #
Former Cuban rafter Yanepsi Santos (right), and her daughter Shirley, pose at the National Medical Institute, a school to train medical personnel that she owns and runs in Miami on September 14, 2014. Santos was a fourth-year medical student and six months pregnant with Shirley when she climbed into a raft in 1994. She spent three days at sea under constant rain before being picked up by the U.S. Coast Guard and taken to Guantanamo Base, where her daughter was born. (Reuters/Enrique de la Osa) #
Former Cuban rafter Pedro Brea, 50, poses while working as a municipal garbage collector in Miami on September 18, 2014. Brea said he spent three days clinging to a sinking raft in the middle of a storm when a U.S. Navy frigate picked him up from the sea in 1994.(Reuters/Enrique de la Osa) #
Former Cuban rafter Jose Ramon Velazquez, 60, poses in one of his optical stores in Miami on September 22, 2014. Velazquez said he was a radiologist when he decided to climb into a makeshift boat with 22 other migrants in 1994. (Reuters/Enrique de la Osa) #
Former Cuban rafter Gricel Gonzalez, 37, at the campaign headquarters of Democratic candidate for the governor of Florida, Charlie Crist, where she works as a communications director in Miami on September 14, 2014. Gonzalez was 16 when she boarded a boat in Cuba with her sister, mother and stepfather to try and reach the Guantanamo Base during the 1994 Cuban Exodus. She said that at night they heard a man crying for help for a pregnant woman, but they never saw them. (Reuters/Enrique de la Osa) #
Former Cuban rafter Hanoi Lopez, 39, in the yard where he works as mechanic at a public school bus company in Miami on September 15, 2014. (Reuters/Enrique de la Osa) #
Former Cuban rafter Moraima Alfonso, 51, in the America TV dressing room where she works as a makeup artist in Miami, on September 17, 2014. Alfonso said she spent ten days at sea and was suffering hallucinations when she was picked up by the U.S. Coast Guard in 1994. (Reuters/Enrique de la Osa) #
Former Cuban rafter Faustino Jose, 60, poses in his jewellery store in Miami on September 16, 2014. Faustino, who was an industrial engineer in Cuba, said he studied all of Thor Heyerdahl's books about rafting before building his own and leaving Cuba in 1994.(Reuters/Enrique de la Osa) #
Former Cuban rafter Tomas Curbelo, 51, in the headquarters of his electrical contracting company in Miami on September 18, 2014. Curbelo said he was jailed in Cuba for being a member of the opposition Democratic Solidarity Party. (Reuters/Enrique de la Osa) #
Former Cuban rafter Sergio Lastres, 49, at an exhibition of his work based on the 1994 Cuban raft exodus in Miami, on September 19, 2014. Lastres and his wife were among 15 migrants rescued when their raft filled with water in 1994. They were taken to Guantanamo Base where he painted his first work about rafters, he said. (Reuters/Enrique de la Osa) #
Former Cuban rafter Veronica Cervera, 42, in her office where she works as a sales representative for a major book publisher, in Miami on September 15, 2014. (Reuters/Enrique de la Osa) #
Former Cuban rafter Carlos Hernandez, 45, in his workshop in Miami on September 18, 2014. Hernandez said he was a youth baseball star in Cuba when he decided to climb into a catamaran in 1994 and head for the U.S. (Reuters/Enrique de la Osa) :// |
|
|
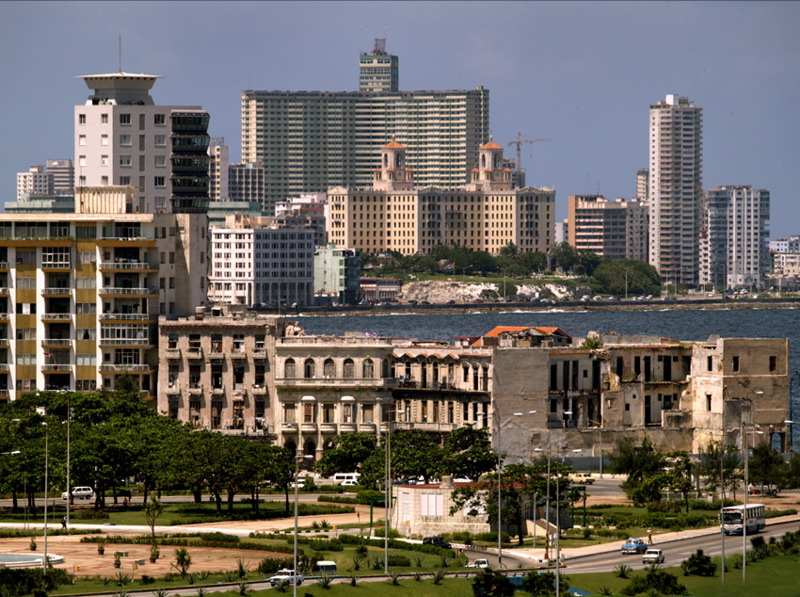










 Article 12 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights states our right to privacy and to a home, denying the state the right to interfere with the process of buying or selling things or owning our home at all.
Article 12 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights states our right to privacy and to a home, denying the state the right to interfere with the process of buying or selling things or owning our home at all.






















































No comments:
Post a Comment